In the fast-paced and often complex world of industrial operations, managing tools efficiently is essential for maintaining productivity, reducing costs, and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Traditional tool management methods, which rely heavily on manual processes, are prone to errors, inefficiencies, and inconsistencies.
This is where Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology steps in, revolutionizing the way we approach tool management. By leveraging RFID tags, readers, and advanced asset tracking software, organizations can automate data collection, enhance real-time visibility, and streamline their operations.
In this article, we will explore the 6 ways RFID technology is transforming tool management, making it more accurate, efficient, and reliable than ever before.
Enhanced Tool Tracking and Inventory Management
Way #1 – Real-Time Location Tracking
One of the most significant advantages of RFID technology in tool management is its ability to provide real-time location tracking. With active RFID tags, large tools and assets can be tracked continuously, even when they are not in use or are stored in various locations. This capability is particularly valuable in environments such as manufacturing facilities, and maintenance operations, where assets are frequently moved or relocated.
For instance, RFID-enabled asset tracking systems can detect the location of tools down to the rack, room, or zone level, ensuring that you always know where your tools are, without the need for manual scanning or audits.
This real-time visibility not only helps in locating tools quickly but also prevents the loss or misplacement of critical equipment. In industries like aerospace and semi-conductors, where tools are often small but highly valuable, UHF RFID tags can be embedded or attached to these tools, enabling precise and continuous tracking. This ensures that tools are always accounted for, reducing downtime and increasing overall operational efficiency.
Way #2 – Automated Inventory Checks
RFID technology also revolutionizes inventory management by automating the process of inventory checks. Traditional methods often involve manual counting and data entry, which are time-consuming and prone to errors.
With RFID, inventory checks can be performed in real-time, using RFID readers placed strategically in receiving and storage areas. These readers can scan multiple RFID tags simultaneously, updating the central warehouse management system with accurate and up-to-date information about the inventory levels and locations of tools.
This automation significantly enhances inventory accuracy, reducing discrepancies between physical stock and recorded data. For example, RFID systems can improve inventory accuracy by up to 95% compared to traditional methods, which is essential for maintaining optimal inventory levels and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Additionally, automated inventory checks eliminate the need for frequent physical audits, saving time and resources that can be better utilized elsewhere in the organization.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Way #3 – Streamlined Check-In/Check-Out Processes
The introduction of RFID technology greatly simplifies the check-in and check-out processes of tools, a fundamental component of tool management. Traditional approaches typically require manual logging, which is not only slow but also susceptible to errors. RFID allows for tools to be automatically checked in and out as they move past designated RFID readers.
This automation eradicates the need for manual data entry, significantly lowering the chances of human errors and conserving precious time for the workforce.
For example, tool carts or RFID cabinets equipped with RFID can automatically record when tools are taken out or put back. This real-time tracking keeps the system constantly updated, offering precise details on tool availability and usage. By making these processes more efficient, the administrative load on employees is lessened, enabling them to dedicate their efforts to more important tasks.
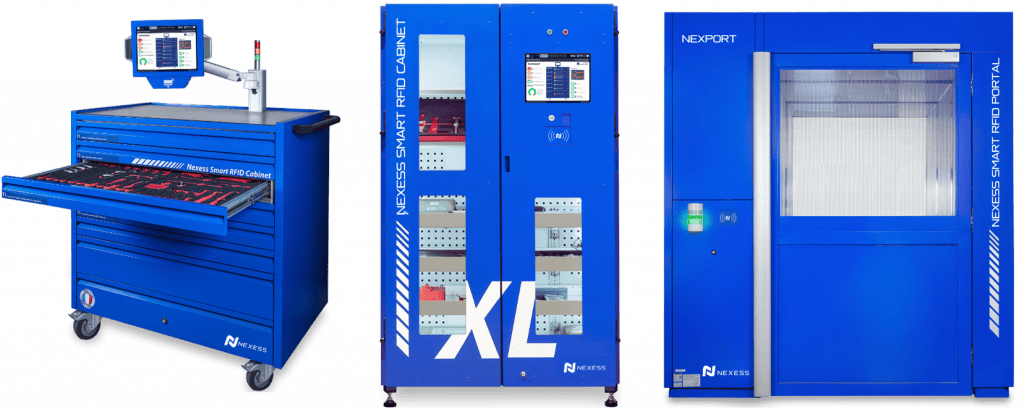
NexCap RFID cabinets and portal streamline check in and chek out of tools with automatic detection of tools
Way #4 – Tool Utilization Analysis
Moreover, RFID technology facilitates a thorough analysis of tool utilization, vital for the optimal allocation of tools and management of resources. Monitoring how tools are used allows organizations to uncover insights into which tools are frequently needed and which are seldom used. This information is essential for making well-informed choices regarding tool acquisition, maintenance, and redistribution.
For instance, RFID systems can monitor how often and for how long tools are used, assisting organizations in identifying tools that are either overused or not used enough. This data can lead to the redistribution of tools to where they are most needed, ensuring that resources are used as efficiently as possible. Furthermore, by analyzing tool usage patterns, maintenance and calibration can be scheduled more effectively, avoiding tool failures and minimizing downtime.
Improved Safety and Maintenance
Way #5 – Enhanced Safety Compliance
RFID technology plays an important role in enhancing safety compliance within various industries. By integrating RFID systems into operational workflows, organizations can ensure adherence to stringent safety regulations and standards. For instance, RFID can be used to track and manage tool calibration dates, ensuring that each tool is properly maintained, inspected, and used according to safety protocols.
This is particularly important in industries like aerospace, energy or transportation where operators and technicians often operate critical tools with predefined torque capabilities.
In addition, RFID systems can be designed to integrate with access control measures, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access certain tools and equipment. This not only enhances workplace safety but also reduces the risk of accidents caused by unauthorized use of critical assets. For example, in aerospace and defense applications,RFID cabinets and tool cartscan be integrated with access control systems to secure sensitive tools, preventing unauthorized access and maintaining strict safety and security protocols.
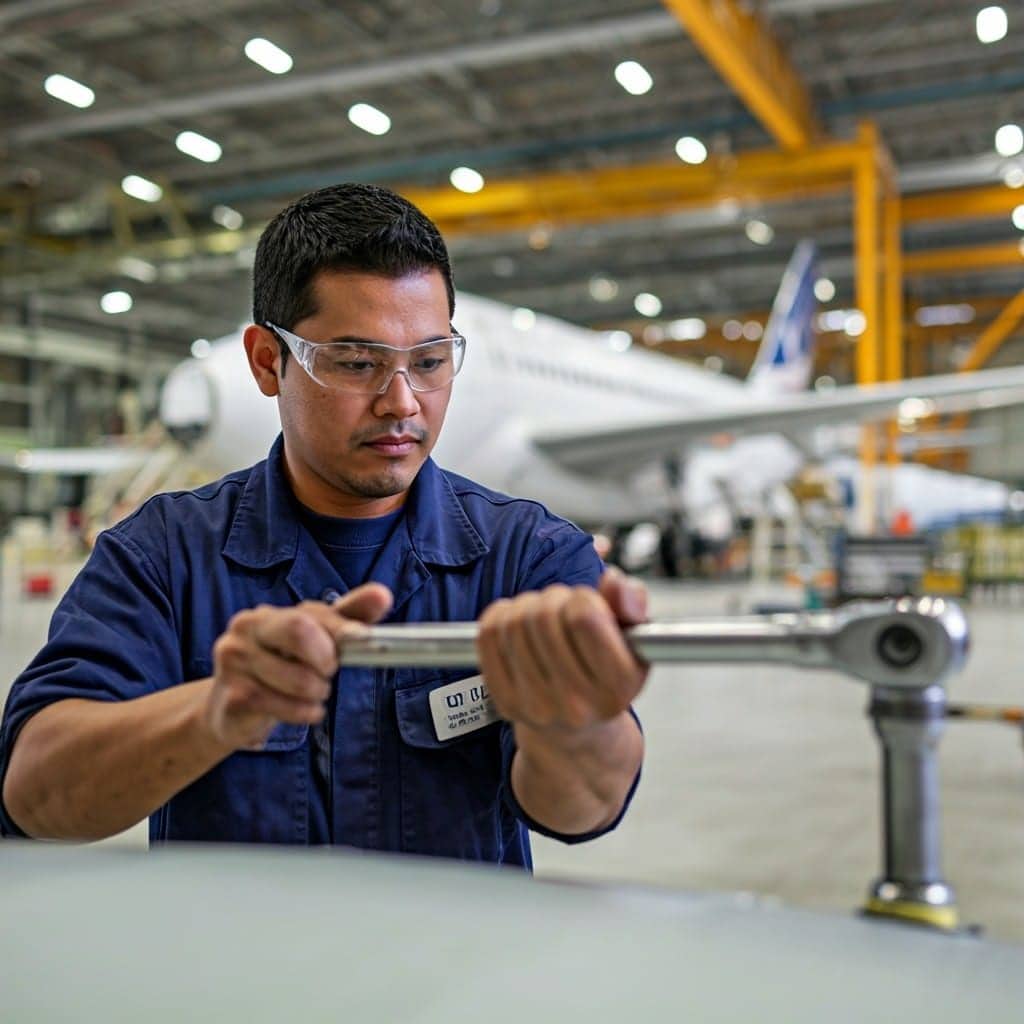

Operator using a torque wrench tracked by RFID
Way #6 – Proactive Maintenance Scheduling
RFID technology significantly improves maintenance practices by enabling proactive maintenance scheduling. By attaching RFID tags to tools and equipment, organizations can track usage, operating hours, and condition in real-time.
This data can be used to automate maintenance scheduling, ensuring that maintenance is performed before potential issues arise. RFID systems integrated with maintenance management software can send automatic alerts to maintenance teams when an asset requires attention, based on predefined triggers such as sensor data indicating anomalies or the completion of a certain number of operating hours.
Condition monitoring is another key aspect of RFID-enabled maintenance. RFID tags equipped with sensors can measure parameters such as temperature, humidity, and vibration, providing real-time insights into the condition of assets. This allows for early detection of wear and tear, enabling proactive maintenance to prevent unexpected failures.
For example, if a machine must be kept within a specific temperature range, RFID sensors can alert maintenance teams if the temperature deviates, ensuring timely intervention to prevent damage or downtime.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RFID technology has transformed the landscape of tool management, offering a plethora of benefits that enhance efficiency, productivity, and safety. Key takeaways include the provision of real-time tool visibility, automated inventory management, and streamlined check-in/check-out processes. RFID systems also improve safety compliance, enable proactive maintenance scheduling, and reduce costs associated with tool loss and theft.
By adopting RFID tool tracking, organizations can optimize their operations, minimize downtime, and ensure strict adherence to regulatory standards. Investing in an RFID tool tracking system is a strategic move towards a more efficient, productive, and safe working environment. Embrace this technology to revolutionize your tool management practices and reap the numerous benefits it has to offer.
FAQ
The core components of an RFID system in tool management consist of:
-
Tags: These emit unique identification information and can be either active or passive.
-
Readers: Devices that read and write data to tags, typically integrated with antennas to facilitate the transmission and reception of radio waves.
-
Antennas: Essential for sending and receiving radio waves between the reader and tags.
-
Controller: Manages communication among the reader, tags, and other elements of the system.
-
Sensors and Actuators: Activate the reader and execute actions based on specific detected conditions.
-
User Interface / Software Application: Processes and displays data from the RFID system.
-
Network Infrastructure: Enables communication between the RFID system and other networks or the internet.
These components collaborate to enable real-time tool tracking, automate inventory management, and boost operational efficiency and safety across various industries
When selecting the appropriate RFID tags for tool tracking, consider the following critical factors:
-
Environment: Opt for tags that are durable and resistant to conditions such as high temperatures, chemicals, or abrasion. Tags with IP68 ratings and resistance to metal interference are particularly suited for challenging environments.
-
Asset Material: Select tags that are compatible with the tools’ material, like on-metal or embedded tags for metal tools.
-
Tag Type: Choose between passive and active tags based on the tool’s value and the necessity for frequent updates. Passive tags are ideal for general tools, while active tags are recommended for high-value items.
-
Read Range and Rate: Ensure the tags possess the required read range and rate for your application, taking into account the speed at which tags move through the read zone and the quantity of tags present simultaneously.
-
Size and Form Factor: Choose tags that match the size and shape of the tools without hindering their functionality, especially for smaller tools.
To optimize tool tracking and management, strategically place RFID readers to ensure complete coverage of the read zone. Position the readers so they directly face the RFID tags, taking into account the layout of the area and the orientation of tagged items.
Employ multiple antennas to address tag orientation challenges and minimize interference. Perform site surveys to identify and rectify potential interference sources.
Adjust the power and gain settings of the readers for optimal performance.
RFID technology enhances tool management by integrating with existing inventory management systems like WMS (Warehouse Management System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). This integration occurs as follows:
-
RFID tags send data to strategically positioned readers, which then forward the information to the central WMS or ERP system, improving real-time inventory visibility and accuracy.
-
This seamless integration facilitates automated data entry and synchronization, reducing manual errors and enhancing supply chain transparency from warehouse to customer.
-
It supports real-time updates of receipts, shipments, and other transactions, and aids in optimizing inventory levels by leveraging historical data and demand forecasts.


 Français
Français



